Improving the odds: Pinpointing the key factors in Thoroughbred pregnancy loss

 CHICKEN MEAT / Thursday, 31 October 2024
CHICKEN MEAT / Thursday, 31 October 2024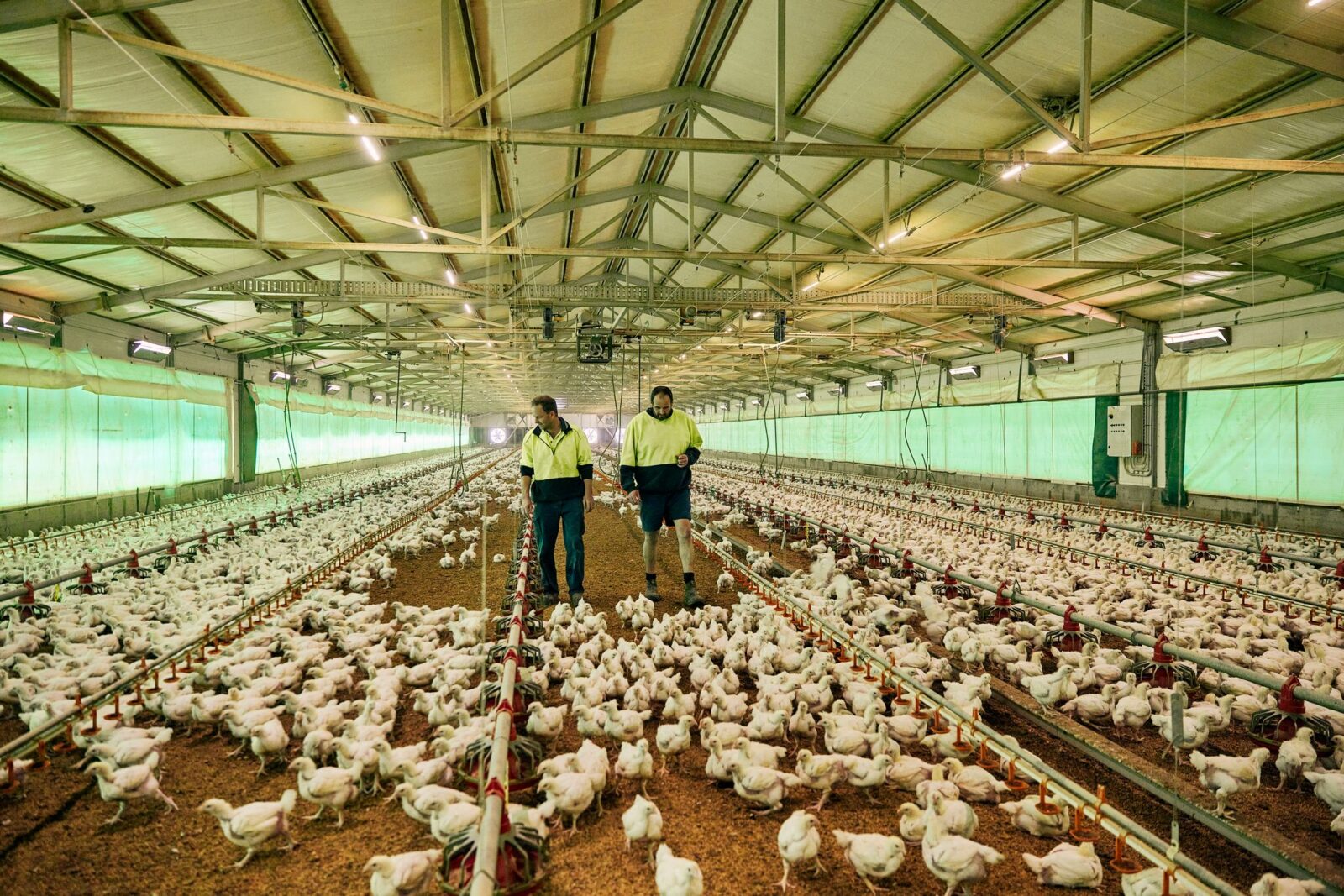 
Through investment in targeted and high-impact projects, the Chicken Meat Program guides investment across the following five priority areas to deliver research, development and extension (RD&E) outcomes to benefit the industry:
In 2023, the Program sought research proposals that were innovative and had the potential to bring transformative change in some of the above priority areas. The Program called for proposals that addressed the current needs and challenges of the chicken meat industry, including an unprecedented period of biosecurity threats and an industry that is continuously striving to strengthen its sustainability credentials.
As a result, the Chicken Meat Program has contracted eight new research projects adding to the thirteen projects already underway in the Program, plus its extension activities. This new suite of projects span three of the five RD&E priorities and are outlined below.
Priority 1: Improving environmental sustainability outcomes
Techno-economic emission reduction pathways for the Australian chicken meat industry (Integrity Ag)
The project will develop the emission reduction pathways for the chicken meat industry, outlining the technologies and strategies, adoption rates, and investment required to meet Federal and customer emission reduction targets. The pathways will be developed in consultation with industry and will be a valuable reference point for the vertically integrated processing companies as they develop their own company-specific emission reduction pathways. Ultimately, the project aims to achieve a consistent approach and methodology across the industry.
Priority 2: Enhancing chicken biosecurity, health and welfare
Using behavioural science to enhance extension and adoption outcomes for the Australian chicken meat industry (Evidn)
The project is employing a behavioural science approach to support the chicken meat industry and its members to adopt better practices for animal health, welfare, and biosecurity. The project aims to enhance biosecurity and animal welfare practices within the chicken meat industry by understanding the factors that influence the workforce’s adoption of these practices. It will involve creating a behavioural science-based training program to upskill the workforce, developing a monitoring and evaluation framework to track progress and identify areas for improvement, and creating a toolkit with evidence-based strategies to support engagement and adoption of industry programs across AgriFutures levied industries
Understanding the biosecurity risk posed by Australian-lineage H5 Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) and the potential genesis to highly pathogenic forms (CSIRO)
Low pathogenicity H5 and H7 avian viruses are frequently detected in Australian wild birds. To date, Australia has had numerous H7 HPAIV outbreaks, but no H5 HPAIV outbreaks; the reason for this is unknown.
The project aims to assess the biosecurity risk posed by Australian-lineage H5N2 viruses by examining their ability to infect and replicate in chickens, performing deep sequencing of infected tissues to identify changes associated with virulence, and using molecular virology techniques to insert key markers of virulence into the genome to determine if these viruses can convert to highly pathogenic forms. Collectively, this information will provide an in-depth biosecurity risk profile of Australian-lineage H5/N2 low pathogenic AIs.
Integrated investigation of Enterococcus cecorum prevalence, transmission Routes, predisposition factors, pathogenic mechanisms, and mitigation strategies in broilers (Central Queensland University)
Enterococcus cecorum (EC) disease outbreaks are a major issue for the broiler industry and animal welfare. Preliminary data shows that these outbreaks are much more complex than a single pathogen outbreak, and that EC is operating in a co-infection mode. Classic amplicon-based microbiota analysis methodology is inadequate as it cannot identify taxonomy at species or strain levels.
The project will use state-of-the-art microbial genomics methodology, with artificial intelligence-assisted prediction and analysis models, to thoroughly interpret every aspect of EC outbreaks.
The research will undertake a deep epidemiological study with the support of significant broiler industry stakeholders, gathering data from several commercial EC outbreaks, identifying and confirming coinfection patterns and mechanisms, mapping virulence factors, achieving a deep understanding of disease pathogenesis, identifying primary spreading sources and triggers, and discovering the ways to minimise damage to the host. This will enable the development of effective mitigation strategies, ultimately improving animal welfare and reducing the economic burden on the industry.
Priority 4: Ensuring the food safety of Australian chicken meat
Poultry spoilage and interventions for shelf life and safety improvements (CSIRO)
The spoilage of chicken meat is a natural process that can be slowed if product is stored under ideal conditions using controlled temperature. Bacteria found on and in live chickens that survive processing eventually can be unavoidably transferred to the surface of chicken meat. Identifying processing equipment to remove spoilage bacteria or reduce contamination levels benefit the industry with improved shelf-life and reduced spoilage associated waste. Any improvements that can be made to ensure that chicken meat has consistent and predictable shelf-life and food safety qualities will limit the risk of reputational, financial, and public health impacts arising from food safety and spoilage events.
This study aims to generate pilot scale information on the effectiveness of Electrostatic Spraying System (ESS) equipment for lowering the overall total viable count (TVC) of whole birds and portions.
Cold-plasma technology: an innovative solution to controlling spoilage and pathogenic foodborne bacteria on chicken meat (University of Adelaide)
Chicken meat processing plants employ various methodologies to mitigate bacteria that include the use of food-grade sanitisers. These methods, however, do not eradicate all bacteria and many can recover following sublethal exposure to sanitisers.
Plasma water has properties, such as low pH and high concentrations of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS), that are highly effective at killing bacteria. Once the RONS have reacted with organic material, they are inactivated leaving behind only pure water. Therefore, plasma water also offers the potential for an eco-friendly approach that eliminates the production of hazardous waste.
The project aims to validate the efficacy of plasma water, an eco-friendly solution that effectively reduces bacterial contamination, ensuring a safer and fresher food product for consumers.
Update on consumer perceptions and handling practices during purchase, preparation, storage and consumption of chicken meat (University of Adelaide)
Previous survey results indicate that the Australian consumers were satisfied with the safety and eating quality of chicken meat and did not have strong concerns about the impact of chicken meat production on animal welfare and the environment.
As part of this project, a consumer survey will be conducted to gain current insights into consumer usage, handling of chicken meat after purchase, and attitudes toward chicken meat safety. The project will help the industry understand the current food safety drivers for chicken meat, and the consumer’s perception about chicken meat food safety.
Priority 5: Building people capability and a diverse and sustainable workforce
Given the importance of chicken meat to consumers and the Australian economy, it is critical for the industry to understand its true economic value in Australia, and extend this beyond just farmgate value.
Input-Output modelling, which estimates the industry’s “contribution” to employment and gross domestic product, will be used to assess the industry’s value, complimented by computable general equilibrium (CGE) models, which assess the industry’s broader impact on the economy. This is particularly useful in the context of the chicken meat industry because the industry is unique in Australian agriculture.
Learn more about the industry’s Chicken Meat Program and it’s RD&E Plan
Keep up to date with news and opportunities from the AgriFutures Chicken Program
 THOROUGHBRED HORSES / 31.10.24
THOROUGHBRED HORSES / 31.10.24  GLOBAL INNOVATION NETWORKS / 31.10.24
GLOBAL INNOVATION NETWORKS / 31.10.24  WORKFORCE AND LEADERSHIP / 31.10.24
WORKFORCE AND LEADERSHIP / 31.10.24  CHICKEN MEAT / 31.10.24
CHICKEN MEAT / 31.10.24